Multidimensional formats, including netCDF, GRIB, and HDF, are often used in the scientific community to store meteorological and oceanographic data such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and direction. Data is normally stored as variables, where each variable is a multidimensional array that represents data captured at multiple times, and at multiple heights or pressures. The multidimensional mosaic dataset can be used to manage and process multidimensional data. See Creating a multidimensional mosaic dataset for step-by-step instructions.
ArcGIS Pro supports three multidimensional raster types—netCDF, GRIB, and HDF—which correspond to multidimensional raster data stored in those formats.
- GRIB—General Regularly-distributed Information in Binary
 is a concise data format commonly used in meteorology to store historical and forecast weather data. The GRIB raster type allows you to add GRIB 1 and GRIB 2 data into a mosaic dataset.
is a concise data format commonly used in meteorology to store historical and forecast weather data. The GRIB raster type allows you to add GRIB 1 and GRIB 2 data into a mosaic dataset. - HDF—Hierarchical Data Format
 is a format designed by the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) to store scientific data. The HDF raster type allows you to add raster data stored in HDF5 or HDF4 into a mosaic dataset. Nonraster data stored in an HDF file is ignored by the HDF raster type.
is a format designed by the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) to store scientific data. The HDF raster type allows you to add raster data stored in HDF5 or HDF4 into a mosaic dataset. Nonraster data stored in an HDF file is ignored by the HDF raster type. - netCDF—Network Common Data Form is a file format for storing multidimensional data. See Fundamentals of netCDF for more information. Currently, netCDF raster types support Climate and Forecast (CF)
 and Cooperative Ocean/Atmosphere Research Data Service (COARDS) conventions. NetCDF files created using other conventions may work but are not supported.
and Cooperative Ocean/Atmosphere Research Data Service (COARDS) conventions. NetCDF files created using other conventions may work but are not supported.
When you define a raster type, specify one of the following processing templates:
- Default—The raster data will be added to the mosaic dataset without any change in pixel value.
- Vector Field—Add raster data representing flow, direction, and magnitude. The mosaic dataset created with this template is visualized using the Vector Field renderer.
- Custom—Your custom template.
Specify variables to add to the mosaic dataset.
You can save a raster type with the variable defined as a raster type template by clicking the Save As button on the General tab so you can reuse it within your organization.
Raster types supported by ArcGIS Pro are listed in the Raster Type drop-down list on the Add Rasters To Mosaic Dataset tool. If your organization has created its own raster type, or if you have modified the properties for a raster type and saved it, you may need to browse to the *.art file to choose it.
Mosaic datasets can manage one or multiple variables. Whether you should put all variables in one mosaic dataset or create one mosaic dataset per variable depends on the application.
- If your application only uses one variable, or a few independent variables, one mosaic per variable is easy to create, use, and manage.
- If your application involves computing from multiple variables using a raster function template, you need to add all the variables used by the template in one mosaic.
- If you want to serve scientific data and want to minimize the number of services, you can add multiple variables to a mosaic and use the variable selector template to access each variable.
Here is an example of computing new data from multiple variables. First, add three variables—temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed—to a mosaic dataset. From these variables, you can construct a raster function template to compute wind chill index and heat index, and add the templates to the mosaic dataset. With the additional three default variable selector templates, you will be able to visualize temperature, wind speed, humidity wind chill, and heat index.
You can use the Groupname field when querying variables at a specific depth and location. The Groupname field defines the groups for items in a mosaic dataset. Items with the same Groupname value belong to one group. A raster function template of item group type will compute from the variables within each group and generate a raster for each group.
Sometimes one item will participate in the computations of all groups. In this case, instead of duplicating this item to each group, set the Groupname for that item as * and with valid values for Tag and Variable fields.
Note:
Multidimensional data does not need to reside in a mosaic dataset. Make sure that a mosaic dataset is appropriate for your workflow.
NetCDF and HDF
Some netCDF or HDF data stores its geolocation as irregularly spaced arrays. When adding to a mosaic dataset, the data is automatically converted to square pixels for display purposes only. The cell size is estimated, but you can change this in addition to setting an interpolation method. Supported interpolation methods include:
- Nearest Neighbor
- Bilinear
- Linear Tinning
- Natural Neighbor
GRIB
Some GRIB products store variables using a parameter code instead of an actual name. A GRIB TAB file with the extended metadata information is required to serve as an interpreter for the code. The text file—normally provided by the organization who produced the data—has a .TAB extension and contains the parameter code, name, center, subcenter, and the table version that produce the data. For example, NASA’s NLDAS dataset requires a GRIB TAB file to interpret variable code 153. The GRIB TAB file that accompanies the data looks like the example below.

Where:
153 is the code
CONVfract is the variable name
The text after the variable name is the long name
7 is the data center
12 is the data subcenter
130 is the table version
When you add NLDAS data to a mosaic dataset using GRIB raster type, you will see a variable is defined as VAR153.
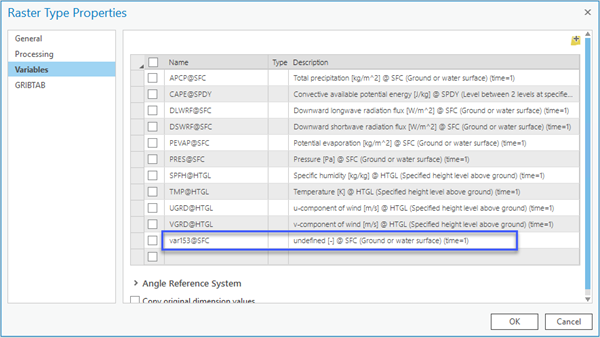
Click the GRIBTAB in the Raster Type Properties, add the GRIB TAB file or the folder that stores all the GRIB TAB files for your datasets, click the Variables tab again, and you will see that the variable is interpreted correctly in the Description. Add the variables into your mosaic dataset.