Rules are an important component of data quality. When used in conjunction, network rules and attribute rules help maintain data integrity.
Network rules dictate which features can connect or associate in the utility network. These rules are imposed at the dataset level for specific asset groups and asset types. Features can connect and associate as long as feature restrictions are respected and network rules exist to allow such relationships.
All rules are evaluated when the network topology is enabled or validated. Rules are also evaluated when an association is created or imported.
There are several network rule types:
- Junction-edge connectivity
- Junction-junction connectivity
- Edge-junction-edge connectivity
- Structural attachment
- Containment
Manage network rules
There are several tasks to help configure and manage rules for a utility network.
Rules are required by a utility network to enable the network topology. A rule base can be created to allow different types of relationships between network features. You can add rules using the Add Rule and Import Rules tools. Once a rule base is established for a utility network, no features can connect or associate that are not supported by a rule. Existing network rules can be viewed from the Network Properties dialog box.
Explore the following workflows for adding different rule types:
Dive-in:
If two edge elements share the same endpoint and have the same Asset group and Asset type, these features can connect without a user-defined intermediate junction or network rule. In this situation, a system junction is created and connectivity is established when the network topology is validated or enabled.
To delete a rule from a utility network, use the Delete Rule tool. You can delete network rules without disconnecting features or removing associations that use the rule. Caution should be taken when deleting rules that support existing features in a utility network. Existing features that rely on deleted rules are marked with errors when the network topology is enabled to indicate there is no rule to support the relationship. Additionally, features with geometric coincidence are disconnected.
Learn more about how to delete a network rule
Rules can be imported to or exported from a utility network. To learn more, see Import and Export network rules.
Tip:
When working with an enterprise geodatabase, network rules are managed through a database connection to the default branch version. The utility network service should be stopped before you add or delete a network rule. Changes are acknowledged after the service and ArcGIS Pro session have been restarted. Updates to the utility network rules are not reflected in existing named versions until a reconcile operation is performed.
Connectivity rules
Connectivity rules define which features can be geometrically coincident or associated.
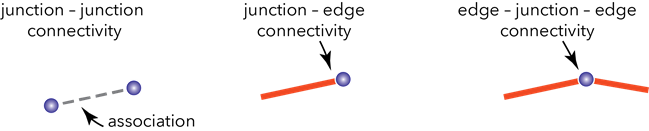
There are three types of connectivity rules:
- Junction-junction connectivity
- Junction-edge connectivity
- Edge-junction-edge connectivity
Junction-junction connectivity rules govern the establishment of a connectivity association between two junction features that are not necessarily geometrically coincident. This rule type supports terminal connectivity. Junction-junction connectivity rules are created between datasets at the asset group and asset type levels—these rules build on top of existing feature restrictions for valid connectivity associations. These rules are evaluated when an association is created. If there is no rule to support the association, an error is returned and the feature is not added to the Modify Associations pane.
Junction-edge connectivity rules govern the types of junction features that can be connected to edge features. These rules build on top of existing feature restrictions for valid geometric coincidence and connectivity associations. Junction-edge rules are evaluated when you enable or validate the network topology.
Junction-edge connectivity rules support line end connectivity to a device or junction object with terminals. Features with terminals cannot be placed midspan. Establishing a connection midspan along a line or edge object to a point or junction object with terminals requires a nonterminal point feature or junction object to be placed midspan, respectively.
In the example below, junction-edge connectivity is established between the midspan tap junction and a medium-voltage line. A junction-junction connectivity association is then established between the midspan tap junction and the high side of the transformer device. Analytic operations travel through the line and the tap point to the connected terminal. 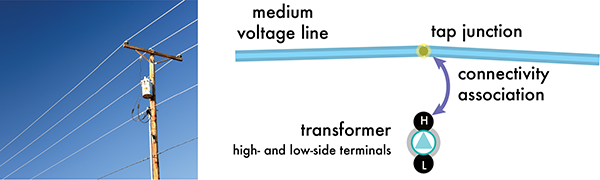
Edge-junction-edge connectivity rules are based on geometric coincidence or connectivity associations. These control the types of line features or edge objects that can be connected using an intermediate junction feature or junction object. Edge-junction-edge connectivity rules are evaluated when you enable or validate the network topology.
The following image shows examples of the three types of connectivity rules:
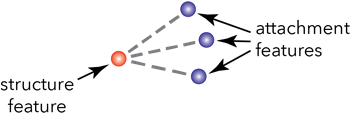
Structural attachment rules
Structural attachment rules constrain the types of features that can be attached to a given type of feature (structure). This rule type does not support terminal connectivity. Structural attachment rules are created between structure features and attachment features. Attachment features can be from the device, junction, assembly, and structure junction feature classes, as well as junction and structure junction object tables. These rules are established at the asset group and asset type levels and build on existing feature restrictions for valid structural attachment associations.
You must assign an appropriate association role to the dataset that will serve as the structure before adding structural attachment rules.
Structural attachment rules are evaluated during edit operations. When attempting to establish an association, the respective list of rules is evaluated to confirm the association is valid. If there is no rule to support the association, an error is returned and the feature is not added to the Modify Associations pane. Edits made to features participating in structural attachment associations are evaluated during enabling or validating the network topology.
The following image shows an example of a structural attachment association:
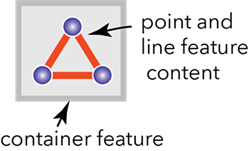
Containment rules
Containment rules constrain the types of features that can be contained in a given type of feature (container). This rule type does not support terminal connectivity. Containment rules are created between datasets at the asset group and asset type levels—these rules build on top of existing feature restrictions for valid containment associations.
You must assign an appropriate association role to the dataset that will serve as the container before adding containment rules.
Containment rules are evaluated during edit operations. When attempting to establish an association, the respective list of rules is evaluated to confirm the association is valid. If there is no rule to support the association, an error is returned and the feature is not added to the Modify Associations pane. Edits made to features participating in containment associations are evaluated during enabling or validating the network topology.
The following image shows an example of a containment association: