Summary
Computes the intersection between two feature classes and cross tabulates the area, length, or count of the intersecting features.
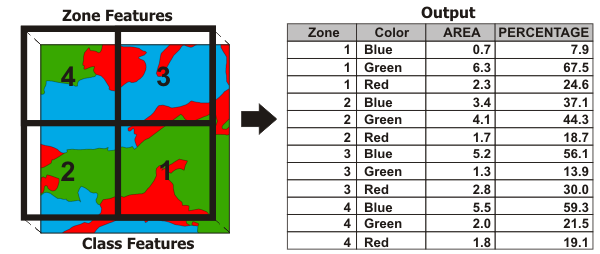
Illustration
Usage
A zone is composed of all features in the Input Zone Features that have the same values in the Zone Fields. Similarly, a class is composed of all features in the Input Class Features that have the same values in the Class Fields. Features do not have to be contiguous to be in the same zone or class. This tool calculates how much of the zone is intersected by each class (area and percentage of zone area).
If no Class Fields value is specified, all features in the Input Class Features will be considered a single class. The Output Table will contain one record for each zone.
If a Class Fields value is specified, the Output Table will contain n records for each zone, where n is the number of classes within that zone. For example, if a zone contains four classes, the Output Table will contain four records for that zone.
Numeric attributes from the Input Class Features can be summed by zone using the Sum Fields parameter. The sum values for a class represent a proportion of the sum values based on the percentage of the class intersecting the zone.
Caution:
Use fields with absolute values (not relative, normalized values such as percentages or densities) as Sum Fields, since the values may be split and apportioned to different zones.
Using a higher dimension Input Class Features than the Input Zone Features is not supported.
- If the Input Zone Features are points, the Input Class Features cannot be polygons or lines.
- If the Input Zone Features are lines, the Input Class Features cannot be polygons.
When the Input Zone Features and Input Class Features are polygons, the output table statistics will be based on area calculations.
When the Input Class Features are lines, the output table statistics will be based on linear calculations.
When the Input Class Features are points, the output table statistics will be based on feature count.
When the Input Zone Features and the Input Class Features are the same dimension (both polygon, both line, or both point), the output PERCENTAGE field records the percentage of the zone feature that is intersected by the class.
If the Input Zone Features and the Input Class Features are different dimensions (polygon zone with line class, polygon zone with point class, or line zone with point class), the output PERCENTAGE field records the percentage of the class intersecting the zone polygon.
It is possible for the PERCENTAGE field to record a percent value greater than 100 when there are overlapping features in the Input Zone Features or the Input Class Features.
The AREA field is included in the output table only when the Input Zone Features and Input Class Features are polygon. The AREA field contains the area of the Input Zone Features that the Input Class Features intersect.
A LENGTH field is included in the output table when the Input Class Features are lines. The LENGTH field contains the length of intersection between the Input Zone Features and the Input Class Features.
A PNT_COUNT field is included in the output table when the Input Class Features are points. The PNT_COUNT field contains the number of Input Class Features points that intersect the Input Zone Features.
When using feature layers, if any features are selected, only the selected features are used in calculations.
Determining the intersection of zone and class features follows the same rules as the Intersect tool.
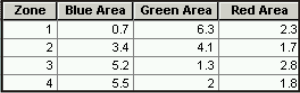
Use the Pivot Table tool to transform the Output Table into a table that contains one record for each zone with class attributes as separate attribute fields. Fill in the parameters for the Pivot Table tool as follows:
- Input Table—Tabulate Intersection Output Table
- Input Fields—Tabulate Intersection Zone Fields
- Pivot Field—Tabulate Intersection Class Fields
- Value Field—Tabulate Intersection Sum Fields or AREA, LENGTH, PERCENTAGE
Syntax
TabulateIntersection(in_zone_features, zone_fields, in_class_features, out_table, {class_fields}, {sum_fields}, {xy_tolerance}, {out_units})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_zone_features | The features used to identify zones. | Feature Layer |
zone_fields [zone_fields,...] | The attribute field or fields that will be used to define zones. | Field |
in_class_features | The features used to identify classes. | Feature Layer |
out_table | The table that will contain the cross tabulation of intersections between zones and classes. | Table |
class_fields [class_fields,...] (Optional) | The attribute field or fields used to define classes. | Field |
sum_fields [sum_fields,...] (Optional) | The fields to sum from the Input Class Features. | Field |
xy_tolerance (Optional) | The distance that determines the range in which features or their vertices are considered equal. By default, this is the XY Tolerance of the Input Zone Features. Caution:Changing this parameter's value may cause failure or unexpected results. It is recommended that this parameter not be modified. It has been removed from view in the tool dialog. By default, the input feature class's spatial reference x,y tolerance property is used. | Linear Unit |
out_units (Optional) | The units to be used to calculate area or length measurements. Setting output units when the input class features are points is not supported.
| String |
Code sample
Use TabulateIntersection in the Python window to find the area of each vegetation type in each zone.
import arcpy
arcpy.TabulateIntersection_analysis("Zones", "zone_id", "Vegetation",
r"C:\Esri\veganalysis.gdb\vegtypeAreas",
"VEGTYPE")This script wraps TabulateIntersection to create a simple TabulateArea script tool. The TabulateArea script tool will only take polygon features as input.
The Zone and Class fields are restricted to one each.
'''
TabulateArea.py
Description: Shows how to wrap the TabulateIntersection tool to create a TabulateArea script tool
Requirements: Polygon Zone Feature Class, Polygon Class Feature Class
'''
import arcpy
import sys
import os
def AddMsgAndPrint(msg, severity=0):
# Adds a Message (in case this is run as a tool)
# and also prints the message to the screen (standard output)
#
print(msg)
# Split the message on \n first, so that if it's multiple lines,
# a GPMessage will be added for each line
try:
for string in msg.split('\n'):
# Add appropriate geoprocessing message
#
if severity == 0:
arcpy.AddMessage(string)
elif severity == 1:
arcpy.AddWarning(string)
elif severity == 2:
arcpy.AddError(string)
except:
pass
## Get Parameters
zoneFC = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
zoneFld = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1) # Only allow one field
classFC = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2)
outTab = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(3)
classFld = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(4) # Optional and only allow one field
sum_Fields = ""
xy_tol = ""
outUnits = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(5)
## Validate parameters
# Inputs can only be polygons
zoneDesc = arcpy.Describe(zoneFC)
classDesc = arcpy.Describe(classFC)
if zoneDesc.shapeType != "Polygon" or classDesc.shapeType != "Polygon":
AddMsgAndPrint("Inputs must be of type polygon.", 2)
sys.exit()
# Only one zone field and class field
if zoneFld != "":
if zoneFld.find(";") > -1 or classFld.find(";") > -1:
AddMsgAndPrint("A maximum of one zone and/or class field is allowed.", 2)
sys.exit()
## Run TI with restricted parameters
try:
arcpy.TabulateIntersection_analysis(zoneFC, zoneFld, classFC, outTab,
classFld, sum_Fields, xy_tol, outUnits)
except:
arcpy.AddMessage("Tabulate Intersection Failed.")
AddMsgAndPrint(arcpy.GetMessages(), 0)Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: No
- Standard: No
- Advanced: Yes