Illustration
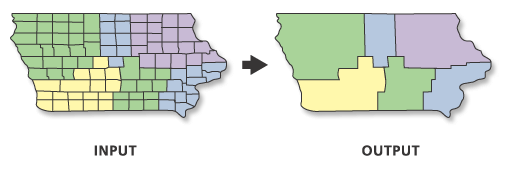
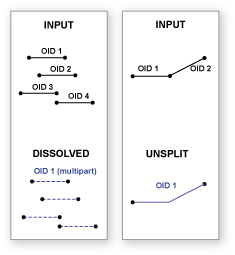
Usage
The attributes of the features that become aggregated by dissolve can be summarized or described using a variety of statistics. The statistic used to summarize attributes is added to the output feature class as a single field with the naming standard of statistic type + underscore + input field name. For example, if the SUM statistic is used on a field named POP, the output will have a field named SUM_POP.
Dissolve can create very large features in the output feature class. This is especially true when there is a small number of unique values in the Dissolve Field(s) parameter or when dissolving all features into a single feature. Very large features may cause processing or display problems or have poor performance when drawn on a map or when edited. Problems may also occur if the dissolve output created a feature at the maximum size on one machine, and this output was moved to a machine with less available memory. To avoid these potential problems, use the Create multipart features parameter to create single part features to split potentially larger multipart features into many smaller features. For extremely large features created by the Dissolve tool, the Dice tool can be used to split the large features to solve processing, display, or performance problems.
Null values are excluded from all statistical calculations. For example, the average of 10, 5, and a null is 7.5 ((10 + 5) / 2). The count returns the number of values included in the statistical calculation, which in this case is 2.
This tool will use a tiling process to handle very large datasets for better performance and scalability. For more details, see Geoprocessing with large datasets.
The availability of physical memory may limit the amount (and complexity) of input features that can be processed and dissolved into a single output feature. This limitation could cause an error to occur, as the dissolve process may require more memory than is available. To prevent this, Dissolve may divide and process the input features using an adaptive tiling algorithm. To determine the features that have been tiled, run the Frequency tool on the result of this tool, specifying the same fields used in the dissolve process for the Frequency Field(s) parameter. Any record with a frequency value of 2 has been tiled. Tile boundaries are preserved in the output features to prevent the creation of features that are too large to be used by ArcGIS.
Caution:
Running Dissolve on the output of a previous dissolve run will rarely reduce the number of features in the output when the original processing divided and processed the inputs using adaptive tiling. The maximum size of any output feature is determined by the amount of available memory at run time; therefore, output containing tiles is an indicator that dissolving any further with the available resources would cause an out-of-memory situation or result in a feature that is unusable. Additionally, running the Dissolve tool a second time on output that was created this way may result in very slow performance for little to no gain and may cause an unexpected failure.
The Unsplit lines parameter only applies to line input. When the default is specified, lines are dissolved into a single feature; otherwise, only two lines that have a common endpoint (known as a pseudonode) are merged into one continuous line.
If the Input Features geometry type is either point or multipoint and Create multipart features is checked (MULTI_PART in Python), the output will be a multipoint feature class. Otherwise, if Create multipart features is unchecked (SINGLE_PART in Python), the output will be a point feature class.
Syntax
Dissolve(in_features, out_feature_class, {dissolve_field}, {statistics_fields}, {multi_part}, {unsplit_lines})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_features | The features to be aggregated. | Feature Layer |
out_feature_class | The feature class to be created that will contain the aggregated features. | Feature Class |
dissolve_field [dissolve_field,...] (Optional) | The field or fields on which to aggregate features. | Field |
statistics_fields [[field, {statistic_type}],...] (Optional) | Specifies the numeric field containing attribute values used to calculate the specified statistic. Multiple statistic and field combinations may be specified. Null values are excluded from all statistical calculations. Text attribute fields can be summarized using first and last statistics. Numeric attribute fields can be summarized using any statistic. Available statistics types are as follows:
| Value Table |
multi_part (Optional) | Specifies whether multipart features are allowed in the output feature class.
| Boolean |
unsplit_lines (Optional) | Controls how line features are dissolved.
| Boolean |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the Dissolve tool in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/Portland.gdb/Taxlots"
arcpy.Dissolve_management("taxlots", "C:/output/output.gdb/taxlots_dissolved",
["LANDUSE", "TAXCODE"], "", "SINGLE_PART",
"DISSOLVE_LINES")The following stand-alone script demonstrates how to use the Dissolve tool.
# Name: Dissolve_Example2.py
# Description: Dissolve features based on common attributes
# Import system modules
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/Portland.gdb/Taxlots"
# Set local variables
inFeatures = "taxlots"
tempLayer = "taxlotsLyr"
expression = arcpy.AddFieldDelimiters(inFeatures, "LANDUSE") + " <> ''"
outFeatureClass = "C:/output/output.gdb/taxlots_dissolved"
dissolveFields = ["LANDUSE", "TAXCODE"]
# Execute MakeFeatureLayer and SelectLayerByAttribute. This is only to exclude
# features that are not desired in the output.
arcpy.MakeFeatureLayer_management(inFeatures, tempLayer)
arcpy.SelectLayerByAttribute_management(tempLayer, "NEW_SELECTION", expression)
# Execute Dissolve using LANDUSE and TAXCODE as Dissolve Fields
arcpy.Dissolve_management(tempLayer, outFeatureClass, dissolveFields, "",
"SINGLE_PART", "DISSOLVE_LINES")Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Yes
- Standard: Yes
- Advanced: Yes