Summary
Creates a big data connection file (.bdc) and item. Datasets registered in a big data connection (BDC) can be used as input to GeoAnalytics Desktop tools and other geoprocessing tools.
Usage
Use this tool to establish a connection to one or more datasets that you can use as input to geoprocessing tools.
Big data connections support the following datasets:
- Delimited files (such as .csv, .tsv, and .txt)
- Shapefiles (.shp)
- Parquet files (.gz.parquet)
Note:
Only unencrypted parquet files are supported.
- ORC files (orc.crc)
To learn more about supported file types, see An overview of the Big Data Connections toolset.
To use your datasets as inputs in a BDC, the data must be correctly structured. To prepare your data for a BDC, format your datasets as subfolders under a single source folder that you register. In this source folder, the names of the subfolders represent the dataset names.
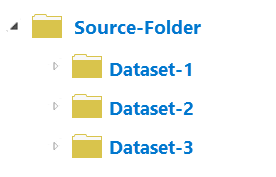
A source folder that contains three subfolders, each representing a dataset, is shown. The image above represents the correct structure of a BDC. The source folder is registered, and each subfolder in the source folder represents a dataset. In this example, you would register the source folder, and three datasets would be included in the BDC: Dataset-1, Dataset-2, and Dataset-3.
Specify the source location from which you want to create a BDC using the Data Source Folder parameter.
A BDC can be stored locally on your machine or on a network drive. If you are sharing a BDC, ensure that you use a source location that all users can access. It is recommended that you not store a BDC in the source folder.
To access a BDC in a project, add the location of the stored BDC as a folder connection.
Setting the geometry or time visibility does not remove geometry or time from the datasets. The time and geometry settings will always apply. For example, if you have a point dataset with geometry represented by two fields, latitude and longitude, the following outlines how the visibility setting will work with your dataset:
- Visible—the latitude and longitude fields will be available in geoprocessing tool parameters and results.
- Not Visible—The latitude and longitude fields will not be available in geoprocessing tool parameters or in the output results.
In both cases, the dataset will have geometry defined by the latitude and longitude fields.
It is recommended that you set geometry fields to Not Visible when you are using long string values such as WKT to represent geometry.
Manually modifying a .bdc file is not recommended. A .bdc file contains the following properties:
- Connection information—The source path
- Dataset information—The dataset names and types, fields, geometry, and time
The tool messages will include the following information on the datasets discovered and their status:
- Succeeded—New datasets that have been discovered and added to the BDC
- Failed—Datasets that were not successfully added to the BDC
You may run into one of two issues when discovering datasets in your BDC:
- Datasets that you expected are missing. In this case, verify that the path you specified is a source folder that contains subfolders is correct and that it's a supported data type.
- One or more datasets fail to register. If datasets fail to register, you may note some of the following:
Issue Solution Example The dataset is not in the expected format.
Open the file to see if it looks as expected. If the data is structured incorrectly, update and try again.
A .csv file has a few lines and a summary of the data, and then only empty lines.
The schemas of datasets in a folder do not match.
All files in a dataset folder must have the same schema. Open the files to compare the schemas. Resolve any mismatched schemas and try to register the dataset again.
You have one .csv file with 10 fields, and another with 8.
The file types of a dataset in a folder do not match.
All files in a dataset folder must have the same extension (file type). Check the file types of the data source location and remove or relocate any misplaced files.
A shapefile dataset is in the same folder as a parquet file.
You have an unrecognized field format.
This is unlikely but may occur if ORC and parquet use an unexpected format. Ensure that you use valid field formats.
You have a parquet file with an unknown field format.
Once you have created a BDC, you can modify the connection information and datasets using the following tools:
- Copy Dataset From Big Data Connection—Copies a dataset from a BDC to a feature class.
- Duplicate Dataset From Big Data Connection—Creates a view of an existing BDC dataset.
- Refresh Big Data Connection—Checks for any new datasets and add them to the BDC.
- Remove Dataset From Big Data Connection—Removes a dataset from the BDC.
- Update Big Data Connection Dataset Properties—Modifies the properties of an individual BDC dataset.
- Preview Dataset From Big Data Connection—Previews the first ten features in your dataset to verify they are correctly registered.
- Describe Dataset — To to verify that the dataset looks as expected.
This geoprocessing tool is powered by Spark. See Big data connections to learn more about big data connections and how to use them.
Syntax
CreateBDC({bdc_location}, bdc_name, connection_type, {data_source_folder}, {visible_geometry}, {visible_time})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
bdc_location (Optional) | The folder where the .bdc file will be created. | Folder |
bdc_name | The name of the .bdc file to be created. | String |
connection_type | Specifies the type of connection to be created.
| String |
data_source_folder (Optional) | The folder containing the datasets to be registered with the BDC. | Folder |
visible_geometry (Optional) | Specifies whether the fields used to specify the geometry will be visible as fields when the BDC file is used as input to other geoprocessing tools. When the geometry fields are not visible, geometry is still applied to the dataset. The geometry visibility setting can be modified in the BDC.
| Boolean |
visible_time (Optional) | Specifies whether the fields used to specify the time will be visible as fields when the BDC file is used as input to other geoprocessing tools. When the time fields are not visible, time is still applied to the dataset. The time visibility setting can be modified in the BDC.
| Boolean |
Derived Output
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| output_bdc | The .bdc file that is created. | File |
Code sample
The following Python script demonstrates how to use the CreateBDC function.
# Name: CreateBigDataConnection.py
# Description: Establishes a connection to a folder location containing one or
# more datasets. Datasets will be used as input to GeoAnalytics
# Desktop Tools.
#
# Requirements: ArcGIS Pro Advanced License
# Import system modules
import arcpy
# Set local variables
sourceFolder = r"\\FileShare\MyLargeDatasets"
outName = "my_new_BigDataConnection"
outFolder = r"c:\Projects\MyProjectFolder"
time = "TIME_NOT_VISIBLE"
geometry = "GEOMETRY_VISIBLE"
# Execute Create Big Data Connection
arcpy.gapro.CreateBDC(outFolder, outName, "FOLDER", sourceFolder, geometry, time)Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: No
- Standard: No
- Advanced: Yes