A utility network has built-in feature restrictions that are imposed at the class level to help promote data accuracy and correctness. Their purpose is to restrict the valid relationships between datasets and control the types of rules that can be added to a utility network. For example, a device feature cannot be geometrically coincident with another device feature. Feature restrictions are system maintained and cannot be modified or removed.
Features can be connected or associated as long as feature restrictions are respected and network rules exist to allow such relationships.
Network rules provide more control to define valid connectivity or association between features. Rules between features that do not violate feature restrictions can be added or imported into a utility network. To learn more, see Network rules.
Each section below shows the valid relationships that can be configured between datasets.
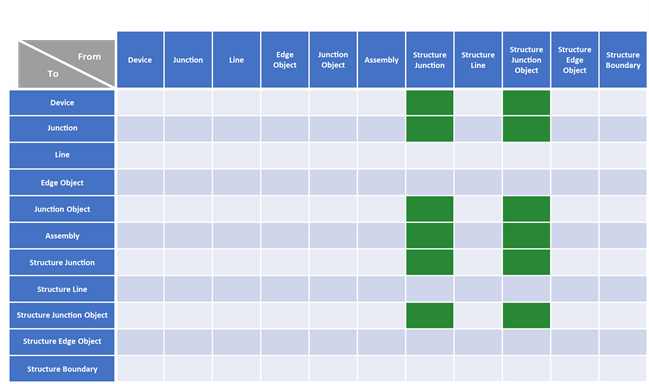
Valid geometric coincidence
Geometric coincident-based connectivity is permitted between a point and line and two lines with an intermediate point feature.
The colored cells indicate valid geometric coincidence between datasets in a utility network; a rule can be created for specific asset groups and asset types.
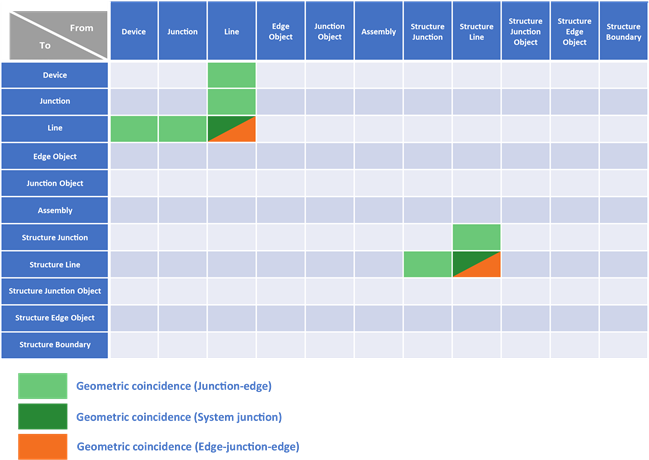
If two edge elements share the same endpoint and have the same Asset group and Asset type, these features can connect without a user-defined intermediate junction or network rule. In this situation, a system junction is created and connectivity is established when the network topology is validated or enabled.
Edge-junction-edge connectivity is established between two edges that are connected by an intermediate junction. The dark orange-colored cells above support edge-junction-edge connectivity between features. The table below lists all supported relationships, including the dataset through which connectivity is established.
Supported edge-junction-edge connectivity between datasets:
| From dataset | To dataset | Via dataset |
|---|---|---|
Line | Line | Device, Junction |
StructureLine | StructureLine | StructureJunction |
Valid connectivity associations
There are several types of connectivity associations permitted between network features.
Colored cells indicate valid connectivity associations between datasets in a utility network; a rule can be created for specific asset groups and asset types.
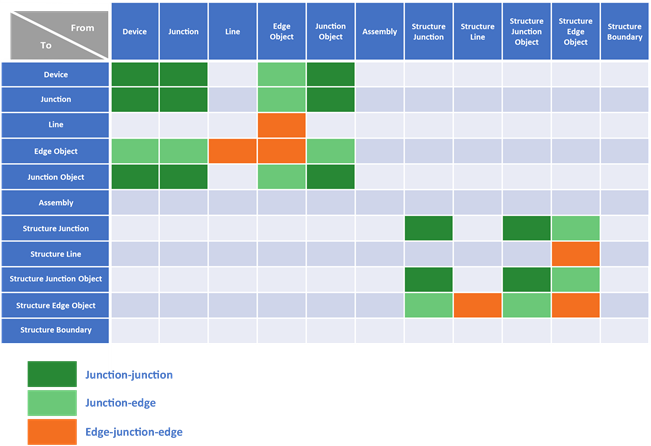
The dark orange-colored cells above support edge-junction-edge connectivity between features. The table below lists all supported relationships, including the dataset through which connectivity is established.
Supported connectivity associations between datasets:
| From dataset | To dataset | Via dataset |
|---|---|---|
Line | EdgeObject | Device, Junction |
StructureLine | StructureEdgeObject | StructureJunction |
EdgeObject | EdgeObject | Device, Junction, JunctionObject |
EdgeObject | Line | Device, Junction |
StructureEdgeObject | StructureEdgeObject | StructureJunction, StructureJunctionObject |
StructureEdgeObject | StructureLine | StructureJunction |
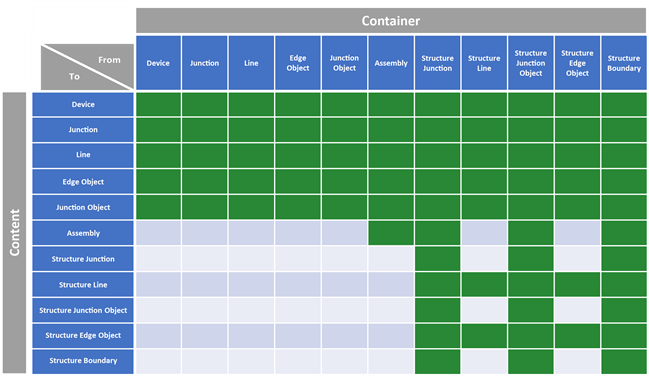
Valid containment associations
In a containment association, features can serve as containers or content.
Colored cells indicate valid containment associations between datasets in a utility network; a rule can be created for specific asset groups and asset types.
Valid structural attachment associations
In a structural attachment association features can serve as a structure or attachment.
Colored cells indicate valid structural attachments between point features or structure junction objects in a utility network; a rule can be created for specific asset groups and asset types.