Available with Advanced license.
Summary
Creates a table from the input table by reducing redundancy in records and flattening one-to-many relationships.
Illustration
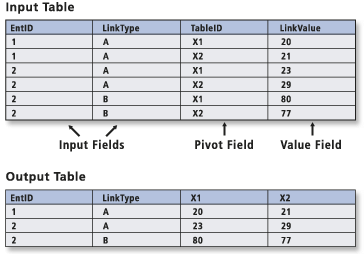
Usage
This tool is typically used to reduce redundant records and flatten one-to-many relationships.
If the Pivot Field is a text field, its values must begin with a character (for example, a2) and not a number (for example, 2a). If the value of the first record begins with a number, all the output values will be 0.
If the Pivot Field is a numeric type, its value will be appended to its original field name in the output table.
The Input Field(s) parameter's Add Field button is used only in ModelBuilder to access and load the expected fields of a preceding process that has not yet been run into the Input Field(s) list so you can complete the Pivot Table dialog box and continue to build the model.
The number of fields in the output table is determined by the number of input fields you choose, plus one field for each unique Pivot Field value. The number of records in the output table is determined by the unique combination of values between your chosen input fields and the pivot field.
The tool fails if the selected Pivot Field contains Null values.
Syntax
arcpy.management.PivotTable(in_table, fields, pivot_field, value_field, out_table)
| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
in_table | The table whose records will be pivoted. | Table View |
fields [fields,...] | The fields that define records to be included in the output table. | Field |
pivot_field | The field whose record values are used to generate the field names in the output table. | Field |
value_field | The field whose values populate the pivoted fields in the output table. | Field |
out_table | The table to be created. | Table |
Code sample
The following Python Window script demonstrates how to use the PivotTable function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
env.workspace = "C:/data"
arcpy.PivotTable_management("attributes.dbf", "OwnerID", "AttrTagNam", "AttrValueS", "C:/output/attribPivoted.dbf")The following Python script demonstrates how to use the PivotTable function in a stand-alone script.
# Name: PivotTable_Example2.py
# Description: Pivot the attributes table by the specified fields
# Author: ESRI
# Import system modules
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Set workspace
env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Set local variables
in_table = "attributes.dbf"
fields = "OwnerID"
pivot_field = "AttrTagNam"
value_field = "AttrValueS"
out_table = "C:/output/attribPivot.dbf"
# Execute PivotTable
arcpy.PivotTable_management(in_table, fields, pivot_field, value_field, out_table)Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: No
- Standard: No
- Advanced: Yes