| Label | Explanation | Data Type |
Input TIN | The input TIN. | TIN Layer |
Output Feature Class | The output feature class. | Feature Class |
Class Breaks Table (Optional) | An input table containing the classification breaks that will be used to classify the output feature class. | Table |
Aspect Field (Optional) | The field containing aspect values. | String |
Summary
Extracts the directional orientation of input TIN to an output polygon feature class.
Legacy:
This is a deprecated tool that has been superseded by the Surface Aspect tool.
Illustration
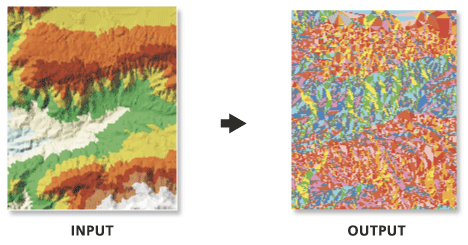
Usage
Aspect is expressed in degrees.
Aspect represents the horizontal orientation of a surface and is determined in units of degrees. Each facet of the surface is assigned a code value which represents the cardinal or ordinal direction of its slope, and contiguous areas with the same code are merged into one feature. The default classification scheme is defined as follows:
Code Slope Direction Slope Angle Range -1
Flat
No Slope
1
North
0° – 22.5°
2
Northeast
22.5° – 67.5°
3
East
67.5° – 112.5°
4
Southeast
112.5° – 157.5°
5
South
157.5° – 202.5°
6
Southwest
202.5° – 247.5°
7
West
247.5° – 292.5°
8
Northwest
292.5° – 337.5°
9
North
337.5° – 360°
Customized class definitions can be provided through a Class Breaks Table. The table must have two columns where the first indicates the aspect break point in degrees and the second defines its code value. Consider the following example:
Break Aspect_Code 90.0
1
180.0
2
270.0
3
360.0
4
The table can be in any supported format (.dbf, .txt, or geodatabase table). The name of the fields are irrelevant, as the first will always be used for the class breaks and the second for the aspect codes.
Parameters
arcpy.ddd.TinAspect(in_tin, out_feature_class, {class_breaks_table}, {aspect_field})| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
in_tin | The input TIN. | TIN Layer |
out_feature_class | The output feature class. | Feature Class |
class_breaks_table (Optional) | An input table containing the classification breaks that will be used to classify the output feature class. | Table |
aspect_field (Optional) | The field containing aspect values. | String |
Code sample
The following Python Window script demonstrates how to use the TIN Aspectfunction in immediate mode.
import arcgisscripting
gp = arcgisscripting.create()
gp.workspace = "C:/data"
gp.TinAspect_3d("tin", "aspect.shp")Environments
Licensing information
- Basic: Requires 3D Analyst
- Standard: Requires 3D Analyst
- Advanced: Requires 3D Analyst