When a relationship class is created with many-to-many cardinality or with attributes, an intermediate relationship class table is created. This table is used to map the associations between the origin and destination objects. The intermediate table contains foreign key fields that are associated with the primary key values from the origin and destination feature classes and/or tables as well as any additional attributes. Each row in the table associates one origin object with one destination object.
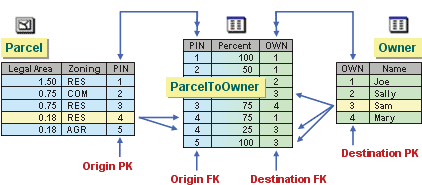
When the intermediate table is created, only the fields are generated for you. ArcGIS does not know which origin objects are associated with which destination objects, so you must manually populate the rows. This can be accomplished in an edit session by selecting related features or rows in the two participating object classes and adding the relationship to the intermediate table via the Attributes dialog box, accessible by clicking the Attributes button  on the Edit tab. Once a relationship has been added to the intermediate table, the foreign key fields will be automatically populated with the related primary key values, and data can be entered in any additional attribute fields. This process must be repeated for all the sets of related features.
on the Edit tab. Once a relationship has been added to the intermediate table, the foreign key fields will be automatically populated with the related primary key values, and data can be entered in any additional attribute fields. This process must be repeated for all the sets of related features.
Note:
When a many-to-many or attributed relationship class is created, a new intermediate relationship class table is created. This intermediate relationship class table is not an object class. As a result, domains, subtypes, contingent values, attribute rules, and default values cannot be used with this type of table.
- Create the relationship class by using the Create Relationship Class geoprocessing tool located in the Data Management Toolbox. Alternatively, if you already have an existing relationship class, connect to the data in the Catalog pane.
- Add the feature classes and/or tables that are participating in the relationship along with the intermediate relationship class table.
- Start editing your data by clicking the Edit tab on the ribbon.
- Interactively select related origin and destination objects using the Select tool
 . If a table is participating in the relationship, open the table and select the desired rows.
. If a table is participating in the relationship, open the table and select the desired rows. - Open the Attributes dialog box by clicking the Attributes button
 on the Edit tab. The selected features will appear in the Attributes pane.
on the Edit tab. The selected features will appear in the Attributes pane. - Expand one of the selected feature classes in the Attributes pane and right-click the relationship class label.
- Click the Add Selected To Relationship option. This will add a row to the intermediate table and populate the foreign key fields with the related primary key values.
- Repeat steps 4 through 7 to populate the relationship class table with all the appropriate relationships between objects.
- Open the relationship class table to view the updated relationships and to input or edit data in the attribute fields.
- You must save your edits to save the relationships and the new data in the intermediate relationship class table.