Web scene layers with associated feature layers allow you to edit and update your data. Depending on the data you are working with and how you configured the web scene layer, you should use different workflows to edit your data.
Editing is available when sharing a web scene layer with an associated feature layer. You have two options when sharing a web scene layer to ArcGIS Enterprise. You can reference registered data from a feature layer in an enterprise geodatabase or a scene layer that copies all data as a hosted feature layer. When sharing a web scene layer that references registered data, the feature class will be nonversioned, have globalIDs, and have archiving enabled. In ArcGIS Online, you can only share a scene layer that copies all data as a hosted feature layer.
Web scene layers that are published from a locally cached scene layer package (.slpk) cannot be edited. Instead, you must delete the web scene layer and share it again. For more information on the differences between web scene layers with associated feature layers and those created from scene layer packages, see What is a scene layer.
The editing workflows described in this topic are supported by ArcGIS Enterprise 10.6.1 and higher and ArcGIS Online.
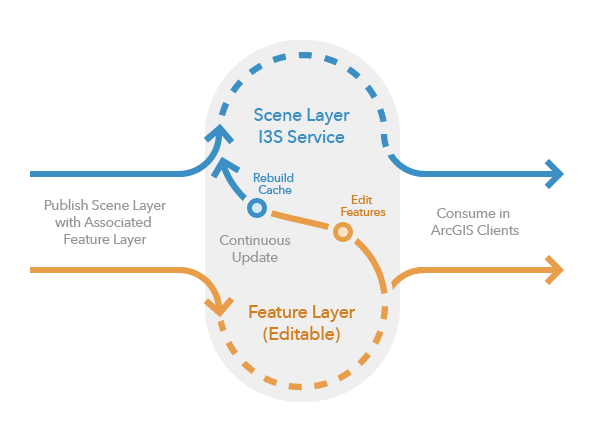
Share an editable web scene layer
If your data requires frequent updates, share a web scene layer with an associated feature layer. ArcGIS Enterprise and ArcGIS Online support editing web scene layers with associated feature layers for 3D object, building and point scene layers.
If you are sharing to an ArcGIS Enterprise portal, it is additionally suggested that your feature data be in an enterprise geodatabase that is registered with a federated server. Although data in a file geodatabase can also be referenced by the associated feature layer, it cannot be edited, and you should either move it to an enterprise geodatabase or copy all data when sharing.
What web layers are editable
| Active portal and data option | ArcGIS Enterprise Reference registered data | ArcGIS Enterprise Copy all data | ArcGIS Online |
|---|---|---|---|
File geodatabase point layer | Noneditable | Editable | Editable |
| Enterprise geodatabase point layer | Editable | Editable | Editable |
| File geodatabase multipatch layer | Noneditable | Editable | Editable |
Enterprise geodatabase multipatch layer | Editable | Editable | Editable |
Revit building layer | Noneditable | Editable | Editable |
File geodatabase building layer | Noneditable | Editable | Editable |
Enterprise geodatabase building layer | Editable | Editable | Editable |
Prepare your data
It is especially important when working with editable web scene layers to ensure that your scene and the layer being shared are in the same coordinate system to prevent shifts in your data or a mismatch in units. For example, if you share a web scene layer that references registered data that is in a projected coordinate system in a global scene, the associated feature layer will be in the projection of your data, while the web scene layer will be in WGS 1984. This is important because edits are saved first in the associated feature layer and then in the web scene layer when it is rebuilt. When you copy all data, both the web scene layer and the associated feature layer are projected to the scene layer's coordinate system. A unit conversion only occurs if your data has a vertical coordinate system. The following steps outline how to prepare your data if sharing a web scene layer that references registered data.
- In the Catalog pane, right-click the Databases folder, click New Database Connection, and connect to the enterprise geodatabase.
- Right-click the feature class you want to share referencing registered data in the enterprise database connection and click Manage.
The Feature Class property dialog box appears.
- Check Global IDs and Archiving and click OK to save your changes and close the dialog box.
Share your data
You can share web scene layers either individually or as part of a web scene. The following steps outline sharing an individual web scene layer. For more information about sharing web scenes, see Share a web scene. If you are sharing to ArcGIS Enterprise, share only the web scene layer so you can choose to reference registered data; otherwise, you can share the web layer as part of the web scene.
- In the Contents pane, right-click a 3D layer, point to Sharing, and click Share as web layer
 .
. - If your active portal is ArcGIS Enterprise and your data is in an enterprise geodatabase, select Scene under Reference registered data.
- Click the Configuration tab and click the configure button
 to configure the associated feature layer.
to configure the associated feature layer.- Check Enable editing and allow editors to and specify what types of edits can be made.
- Uncheck Apply default to features with z-values.
It is strongly suggested that you do not apply a default z-value. Client applications that do not support editing z-values, such as Map Viewer Classic, will override your z-values if you make geometry updates. By not including a default z-value, you ensure that all geometry updates are applied through a client application that supports full 3D editing, such as ArcGIS Pro.
User types, roles, and privileges for scene layers with associated feature layers
When consuming a scene layer with associated feature layer, the access to the layer depends on the privileges the user has in ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise. For example, the user type Editor can edit the scene layer while a Viewer can only view the layer, unless the layer is publicly shared.
Editable scene layers with associated feature layer in your organization
After sharing a scene layer with associated feature layer in your organization, the user roles will define the permissions granted to members of your organization. For example, if a user has Editor or Publisher rights, the scene layer with associated feature layer is editable in ArcGIS Pro for this user. In case a user only has the role of Viewer, the assigned scene layer can only be viewed.
You can access the scene layer with associated feature layer by sharing to a specific group within your organization.
- In the Contents pane, right-click a 3D layer, click Sharing, and click Share as web layer.
- In the Sharing pane, click Share with, and click your organization.
- Click the Groups drop-down menu and select the group you want to share the scene layer with.
Any member of your organization and or member of your group can now edit the scene layer, if permitted. The owner of the scene layer with the associated feature layer always has full access to the data.
Editable scene layer with associated feature layer shared with everyone
If you want to share an editable scene layer with everyone, you must allow data collection. Data collection will allow anyone to edit your data. You may not want to give others edit access to your data.
You can share a scene layer with associated feature layer with everyone without enabling editing. Because the owner and administrator always have access to the data, these users can continue editing the scene layer with associated feature layer. The required dataset properties, such as Archiving and GlobalID, can be set on the feature service using the Admin API.
Keep the following in mind when sharing editable scene layers:
- It is recommended that you set the editing option when sharing the scene layer and, if needed, withdraw the editing and data collection capabilities on the associated feature layer setting or your portal.
- If an editable scene layer with associated feature layer has been shared publicly, you can withdraw the data collection permission. On the detail page of the associated feature layer in your portal home application, uncheck Enable editing and Approve for Public Data Collection. No further steps are required. The administrator and data owner can continue editing the data.
View an editable web scene layer
Since web scene layers are cached layers, you may not see the latest edits made to a web scene layer. Whether you have editing permissions on the web scene layer and what type of data was shared determine when you can view edits and how the web scene layer appears in ArcGIS Pro. Edits made to a web scene layer, whether they are applied through the web scene layer or the associated feature layer, are always first stored with the feature layer and then cached after the web scene layer is rebuilt. Only users who have editing capabilities can see the edits stored with the associated feature layer in addition to the web scene layer.
Note:
When viewing an editable web scene layer in ArcGIS Pro, you receive a notification that the web scene layer is editable, and the data may not be up to date. To ensure you are viewing the latest version of the web scene layer, set a refresh interval on the layer in ArcGIS Pro. This can be done through the layer's general properties page.
View an editable web scene layer without editing permissions
As a user without editing permissions, you can view features drawn from the web scene layer. This means that until the web scene layer is rebuilt to include edits performed by others, the edits stored with the associated feature layer are not visible to you. Because ArcGIS Pro displays the attribute table of the associated feature layer, there may be a mismatch between the values seen in the attribute table, the visible features, and their pop-ups until the owner of the scene layer or administrator rebuilds the cache.
View an editable web scene layer with editing permissions
As a user with editing permissions, you also view features drawn from the web scene layer. When working with point web scene layers that reference registered data or any building or 3D object web scene layer, you additionally see edits that are stored with the associated feature layer, even before the web scene layer is rebuilt. When conducting many edits, you may notice a decrease in drawing performance as more features are drawn from the associated feature layer instead of the web scene layer.
Note:
If too many features have been edited or you select too many features to edit, a warning appears to rebuild the web scene layer. When too many features have to be drawn from the associated feature layer, performance can decrease and features may stop drawing. In some cases, you may notice errors in drawing or in the attribute table. If this occurs, contact your administrator to restart the feature service and rebuild the web scene layer before continuing to make edits.
To view edits made to point web scene layers with their data copied to the server, the web scene layer must be rebuilt to visualize the edits.
When edits can be viewed
| Active portal and data option | ArcGIS Enterprise Reference registered data | ArcGIS Enterprise Copy all data | ArcGIS Online |
|---|---|---|---|
File geodatabase point layer | Noneditable | Visible after the cache is rebuilt | Visible after the cache is rebuilt |
| Enterprise geodatabase point layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible after the cache is rebuilt | Visible after the cache is rebuilt |
| File geodatabase multipatch layer | Noneditable | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer |
Enterprise geodatabase multipatch layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer |
Revit building layer | Noneditable | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer |
File geodatabase building layer | Noneditable | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer |
Enterprise geodatabase building layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer | Visible before the cache is rebuilt from the associated feature layer |
Before the web scene layer is rebuilt, new attribute values will not be automatically recognized. For example, if the layer is symbolized using unique values, the newly added value will need to be added manually. Similarly, to use the value in a definition query, it must be manually typed since it will not display in the list of attribute values.