Available with Image Analyst license.
With the ArcGIS Image Analyst extension, you can perform entire deep learning workflows with imagery in ArcGIS Pro. Use geoprocessing tools to prepare imagery training data, train an object detection, pixel classification, or object classification model, and produce and review results.
Note:
This topic describes deep learning for imagery workflows using Image Analyst. For an overview of all the deep learning capabilities in ArcGIS Pro, see Deep learning in ArcGIS Pro.
The workflow is represented in the diagram below.
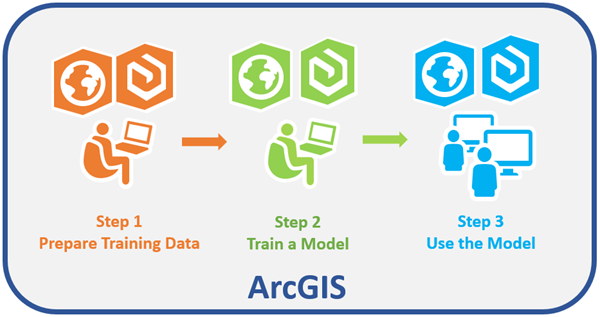
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Create training samples in the Label Objects for Deep Learning pane, and use the Export Training Data For Deep Learning tool to convert the samples into deep learning training data. Note:The Export Training Data For Deep Learning tool is also supported with the Spatial Analyst extension. |
| Use the Train Deep Learning Model tool to train a model using PyTorch, or train the model outside of ArcGIS Pro using a supported third-party deep learning framework. |
| Use the trained model to run the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool, the Classify Pixels Using Deep Learning tool, or the Classify Objects Using Deep Learning tool to generate an output. Review and validate results using the attributes pane, and compute accuracy using the Compute Accuracy For Object Detection tool. |
Features and capabilities
Deep learning tools in ArcGIS Pro allow you to use more than the standard machine learning classification techniques.
- Use convolutional neural networks or deep learning models to detect objects, classify objects, or classify image pixels.
- Integrate external deep learning model frameworks, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras.
- Use a model definition file multiple times to detect change over time or detect objects in different areas of interest.
- Generate a polygon feature class showing the location of detected objects to be used for additional analysis or workflows.
- Take advantage of GPU processing as well as using CPU for distributed processing.
Get started with deep learning
The creation and export of training samples are done in ArcGIS Pro using the standard training sample generation tools. The deep learning model can be trained with the PyTorch framework using the Train Deep Learning Model tool, or it can be trained outside of ArcGIS Pro using another deep learning framework. Once the model is trained, use an Esri model definition file (.emd) to run geoprocessing tools to detect or classify features in your imagery.
You must install the deep learning framework Python packages; otherwise, an error occurs when you add the Esri model definition file to the deep learning geoprocessing tools. For information about how to install these packages, see Install deep learning frameworks for ArcGIS.
- Create and export training samples.
- Use the Label Objects for Deep Learning pane or the Training Samples Manager to select or create a classification schema.
- Create training site samples for the class categories or features of interest. Save the training sample file.
- Run the Export Training Data for Deep Learning geoprocessing tool to convert the source imagery and training samples to deep learning training data. The source imagery can be an image service, a mosaic dataset, a raster dataset, or a folder of rasters. The output of the tool is image chips or samples containing training sites to be used to train the deep learning model. An additional output of the tool is a template .emd file that must be populated.
- Train the deep learning model.
- Use the Train Deep Learning Model tool to train a deep learning model using the image chips generated in the previous step.
- Run the inference geoprocessing tools in ArcGIS Pro.
- Use the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning, Classify
Pixels Using Deep Learning, or Classify Objects Using Deep Learning geoprocessing tool to process your imagery. If the trained model incorporated custom Python raster functions with additional variables, such as padding or a confidence threshold for fine-tuning the sensitivity, these variables appear on the geoprocessing tool dialog box for user input. The data type, such as string or numeric, is specified in the Python raster function. Ideally, additional inference parameters should be limited to two.
The Esri model definition parameter value can be an Esri model definition JSON file (.emd) or a JSON string. A JSON string is useful when this tool is used on the server so you can paste the JSON string rather than upload the .emd file.
The output of the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool is a feature class showing the objects detected by the model. The Classify Pixels Using Deep Learning tool outputs a classified raster. The Classify Objects Using Deep Learning tool requires a feature class and imagery as the input datasets, and the result is a feature class in which each object within each feature is labeled with a class name.
- Use the Detect Objects Using Deep Learning, Classify
Pixels Using Deep Learning, or Classify Objects Using Deep Learning geoprocessing tool to process your imagery. If the trained model incorporated custom Python raster functions with additional variables, such as padding or a confidence threshold for fine-tuning the sensitivity, these variables appear on the geoprocessing tool dialog box for user input. The data type, such as string or numeric, is specified in the Python raster function. Ideally, additional inference parameters should be limited to two.
After using a deep learning model, it's important that you review the results and assess the accuracy of the model. Use the Attributes pane to review the results from your object-based inferencing (Classify Objects Using Deep Learning tool or Detect Objects Using Deep Learning tool). You can also use the Compute Accuracy For Object Detection tool to generate a table and report for accuracy assessment.
To learn about the basics of deep learning applications with computer vision, see Introduction to deep learning.
For information about requirements for running the geoprocessing tools, and issues you may encounter, see Deep learning frequently asked questions.
Developer resources
In addition to the geoprocessing tools and workflows available in ArcGIS Pro, you can also perform deep learning tasks in scripts and notebooks. If you are working in ArcGIS REST API, use the deep learning tasks available with the raster analysis service. These tasks are equivalent to the available geoprocessing tools but allow for distributed processing depending on your processing configuration.
If you are working in ArcGIS API for Python, there are many additional deep learning tasks available with the arcgis.learn module .


