Dive-in:
Most Python script tools that run successfully on your computer will publish and run successfully as a geoprocessing service—you do not have to modify your script. However, if you are encountering problems, it may be due to your script using a lot of project data, which means input data not as a parameter, or using import statements to import Python modules that you developed. In this case, you may find this topic helpful, as it covers the following scenarios:
- How to construct paths to project data and how it is found.
- How imported modules are found and made available for tool use.
- How third-party libraries are handled.
- How tool validation code is handled and its interaction between the client and the geoprocessing service.
If you are unfamiliar with Python, ArcPy, or script tools, skip to the Get started with Python, ArcPy, and script tools section below for a list of useful topics.
How to construct paths to project data and how it is found
An important part of many Python scripts is the proper construction of paths referencing data. This includes project data (input data not exposed as a parameter) found inside scripts, and intermediate (temporary) data. There are different ways to write paths in Python that reference data. See Setting paths to data in Python for details on how a full path should be written.
A path to data relative to a known location can be constructed using os.path.join. This is also useful for constructing paths to output locations that reside in the memory workspace or with using scratch locations for temporary data to disk. See the example below using os.path.join.
When you share your tool as a geoprocessing service, the script is scanned, and every quoted string (either single quotes or double quotes) used in a Python variable or as an argument to a function is tested to see whether it is a path to existing data. Project data, in this case, means the following:
- A layer in the table of contents of your map or scene
- A folder
- A file
- A geodataset, such as a feature class, shapefile, geodatabase, map (.mapx), or layer file (.lyrx)
When a quoted string is found in the script, the test for data existence proceeds as follows:
- Does the string refer to a layer in the Contents pane?
- Does the string contain an absolute path to data (such as "e:\Warehousing\ToolData\SanFrancisco.gdb\streets")?
- Does the string reference data that can be found relative to a known location, such as the project file .aprx or the script?
These tests proceed in sequential order. If the test passes, and the data exists, it will be consolidated, with one exception: if the data has been registered with the portal's federated data store, it will not be consolidated.
Note:
When folders are consolidated, only files and geodatasets within the folder are copied; no subfolders are copied. Some geodatasets, such as file geodatabases and rasters, are technically folders, but they are also geodatasets, so they will be copied. If the folder contains layer files (.lyrx) or maps (.mapx), all data referenced by the layer file or map is also consolidated so that any arcpy.mp routines in the script can gain access to the referenced data.
Tip:
Due to the way folders are consolidated, you should avoid cluttering the folder with large datasets and files that will never be used by your tool; it unnecessarily increases the size of the data to be packaged or uploaded to the server. (This does not apply to folders in a server's data store, as these folders are not uploaded to the server.)
Example
The following example is based on this project folder structure:
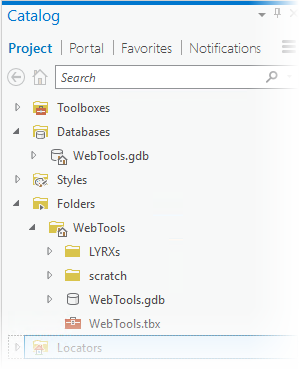
Relative paths to datasets and folders
An arcpy.mp routine provides the ability to get the homeFolder or defaultGeodatabase for a given project. Paths can be built using the Python os module. In the following example, a feature class in the WebTools.gdb geodatabase is set and symbolized using a layer file in the LYRXs folder:
import arcpy
import os
# The ArcGIS Project is used to build paths from the defaultGeodatabase and
# homeFolder using os.path.join
# Reference the CURRENT project with ArcGIS Pro open, or point to an .aprx on
# disk
prj = arcpy.mp.ArcGISProject("CURRENT")
arcpy.CopyFeatures_management(os.path.join(prj.defaultGeodatabase, "study_sites"),
"in_memory/tempSite")
# Create a variable to reference the LYRX folder
lyrxFolder = os.path.join(prj.homeFolder, "LYRXs")
arcpy.ApplySymbologyFromLayer_management("in_memory/tempSite",
os.path.join(lyrxFolder, "Site4.lyrx"))
In the code above, the study_sites feature class and the Site4.lyrx file (and the data it points to) will be tested to see whether they reference data that exists. These datasets will be consolidated and uploaded to the server (unless the folder in which they reside has been referenced as part of the server's data store).
The lyrxFolder variable references a relative path to a folder of layer files. This folder will be consolidated; all of its contents (with the exception of subfolders as noted above) will be packaged or uploaded to the server (unless the lyrxFolder folder is part of the server's data store).
Reference layers as project data
A less common workflow of using layers as project data can result in significant performance improvements for your Python script tool. The above Python code uses full paths to feature classes and layer files. When a geoprocessing service is run, it must first open the dataset, and opening a dataset has a performance cost. Using layers in your script will keep the data opened and cached for faster performance. The following image shows how layers in the project's contents are matched and used in the Python script:
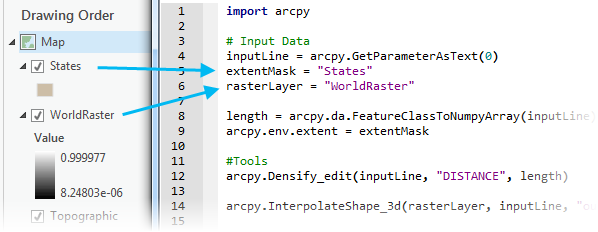
The variables (extentMask and rasterLayer) point to simple strings that match the layer names in the map. The data will be consolidated and available in the geoprocessing service when shared to your portal (if not referenced in the data store) and will hold a reference to the layers in memory. This name matching from the layers in the map to the strings in your script allows tools to work with layers.
Note:
When using layers as internal project data to a script tool, the script tool becomes dependent on the associated map. You cannot run the tool from another map without those layers present. This pattern reduces the general portability of your script tool. As such, this pattern is most suited to creating geoprocessing services.
Import other Python modules
Your script may import other scripts that you developed. For example, the following code shows importing a Python module named myutils.py, which is in the same directory as the parent script and contains a routine named getFIDName:
import arcpy
import myutils
inFeatures = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
inFID = myutils.getFIDName(inFeatures)
When an import statement is encountered, the following order is used to locate the script:
- The same folder as the script. If the script is embedded in the toolbox, the folder containing the toolbox is used.
- The folder referenced by the system's PYTHONPATH variable.
- Any folder referenced by the system's PATH variable.
Another technique for referencing modules to import is to use the sys.path.append method. This allows you to set a path to a folder containing scripts that you need to import.
import arcpy
import sys
import os
# Append the path to the utility modules to the system path
# for the duration of this script.
myPythonModules = r'e:\Warehousing\Scripts'
sys.path.append(myPythonModules)
import myutils # A Python file within myPythonModules
In the above code, note that the sys.path.append method requires a folder as an argument. Since r'e:\Warehousing\Scripts' is a folder, the entire contents of the folder will be consolidated. The rules for copying folder contents apply here as well—everything in the folder is copied except subfolders that are not geodatasets.
Note:
Python scripts in the folder are not scanned for project data or imported modules.
Third-party modules
Third-party modules and libraries (any module that is not part of the core Python installation) are not consolidated. You must ensure that the module exists and runs correctly on the server. This does not apply to the numpy, matplotlib, and other modules that are installed with your ArcGIS Server by default. To deploy third-party Python modules, see Deploying custom Python packages for ArcGIS Server.
Tool validation code
If you have experience writing script tools, you may be providing your own tool validation logic. Clients of geoprocessing services do not have the capability to run your tool validation logic—only the server has this capability. When the clients send their run task request to the service, your validation logic will run on the server. If your validation routines throw an error, the task run will stop. If you're returning messages from your service, the client will receive messages thrown by your validation routines. Generally, tool validation code as part of a published geoprocessing service provides less value than it did to the tool when used on the desktop. You may want to work with a copy of your geoprocessing service that has validation code reduced or removed and share that as a geoprocessing service. You should develop the validation logic in the application to consume the geoprocessing service.
Validation logic is implemented with Python, and your validation code will be scanned for project data and modules, as with any other Python script. For example, your validation logic may open a folder (for example, d:\approved_projections) containing projection files (.prj) to build a choice list of spatial references the client can use when the server runs your tool. This folder is not a tool parameter; it's project data used in your tool validation script. The same rules described above for Python scripts apply here, and the consequence is that the d:\approved_projections folder will be consolidated and copied to the server (unless it's found in the server's data store).
Get started with Python, ArcPy, and script tools
If you are unfamiliar with Python, ArcPy, or script tools, the following table lists topics that will help you get started:
| Help topic | Contents |
|---|---|
Introductory topics to geoprocessing. | |
Introductory topics to ArcPy. | |
Introductory topics on creating custom script tools using Python. | |
Once you've become familiar with the process of creating a script tool, this topic is referred to often, as it explains in detail how to define script tool parameters. |