The StreetMap Premium dataset contains a ready-to-use network dataset and is the same network, whether in mobile map package format (.mmpk file) or file geodatabase format (.gdb file).
Note:
The mobile map package is available in either GCS_WGS_1984 uncompressed or WGS84 Web Mercator (Auxiliary Sphere) compressed formats. The GCS_WGS_1984 uncompressed format is optimized for routing in ArcGIS Pro and routing services in ArcGIS Enterprise. The network dataset is uncompressed for users who require more performant network analysis; the trade-off is a larger dataset due to the data not being compressed. The network dataset for Morocco.mmpk, for example, is extracted to the default location C:\Users\<UserName>\Documents\ArcGIS\Packages\Morocco_<unique#>\commondata folder. The network dataset is made up of the middleeastandafrica.geodatabase (the mobile geodatabase) and the middleeastandafrica.tn folder.
ArcGIS Navigator and ArcGIS Runtime users should continue to use the WGS84 Web Mercator (Auxiliary Sphere) compressed format.
The geographic extent of the network dataset may vary based on the mobile map package that you download or the geography that you license. If you are importing the StreetMap Premium mobile map package format into ArcGIS Pro, the imported map (StreetMap Dark or StreetMap Day) contains the Routing_ND network dataset at the bottom of the Contents pane. This network dataset is available for routing in ArcGIS Pro as long as you are licensed for the ArcGIS Network Analyst extension and the proper regional StreetMap Premium extension. The Routing_ND network dataset can be added to ArcGIS Pro with the Add Data button and is available for network analysis as long as you have the ArcGIS Network Analyst extension (.mmpk format) or the appropriate StreetMap Premium license file (*.sdlic) installed (.gdb format).
For more information about using routing services in ArcGIS Pro, see Create a network analysis layer.
For details on publishing a routing service in ArcGIS Enterprise, see Publish routing services in the ArcGIS Server help.
Routing services
With the Routing_ND network dataset included in StreetMap Premium, you can create routes in ArcGIS Pro using the ArcGIS Network Analyst extension.
In ArcGIS Server, use the Publish Routing Services utility to create a routing service using either the .mmpk format or the .gdb format of the Routing_ND network dataset. After publishing is complete, add the ArcGIS Server connection to your ArcGIS Pro session by clicking the Insert tab, and clicking Connections > Server > Add Server (or New ArcGIS Server if you have not already set up the connection file). After the server connection is added to the Catalog pane, browse to the Network Analysis geoprocessing toolbox to run a geoprocessing tool, such as Find Routes or Generate Service Areas. Double-click the geoprocessing tool or right-click the tool and click Open to start using the tool.
If you are connecting to a federated server through your portal rather than a stand-alone server, go to Catalog > Portal to find your Portal content. Then go to Network Analysis Web Tool and double-click to open. Double-click the geoprocessing tool or right-click the tool and click Open to start using the tool. The published network dataset will also be shown as the network dataset source under the Network Analyst icon along with the available network analysis types (Service Area or Route, for example).
In ArcGIS Enterprise Portal, sign in to your Portal. Under Organization > Settings, find Utility Services. Use the Directions and Routing > Update routing services > Configure routing services dialog box to publish a routing service using the A network dataset I'd like to publish option. The published network dataset will be shown as the network dataset source under the Network Analyst icon along with the available network analysis types (Service Area or Route, for example).
For more details about routing levels, trucking restrictions, and historical, predictive, and live traffic information for each country, see StreetMap Premium product coverage (all products) on the ArcGIS StreetMap Premium website.
The following routing capabilities are defined below: historical traffic data, live traffic data, impedance options, restrictions, and travel modes.
Historical traffic data
You can use historical traffic data by specifying start times when creating routes using the Network Analyst extension. You can also visualize the historical traffic data by using the Time Slider tool. Using historical traffic data results in more accurate travel times, as the data stores traffic flow information by day of the week and time of day. For example, routing through the city at 7:30 a.m. on a weekday takes longer than routing through the city at midnight. Historical traffic is based on the average of observed speeds over the years. A few specific types of links are not covered in historical traffic, because they are not navigable roadways: ferry links, rail links, and any link that is not marked as accessible by emergency vehicles.
Live traffic data
In ArcGIS StreetMap Premium, you have the option to access a live traffic feed through the ArcGIS Online World Traffic Service. Using a live traffic service with ArcGIS StreetMap Premium allows you access to high-quality live and predictive traffic data that can improve the results of Network Analyst functions such as routing. Live traffic as a service is available for an additional fee as part of the ArcGIS StreetMap Premium product. Esri Customer Service will provide access to the ArcGIS Online World Traffic Service through your ArcGIS Online account after purchase.
An ArcGIS StreetMap Premium Live Traffic license and the ArcGIS Network Analyst extension are required to access the live traffic feed.
To configure live traffic, see the Use live traffic from the ArcGIS Online World Traffic Service with ArcGIS StreetMap Premium topic in the ArcGIS Pro help. Live traffic can be configured for ArcGIS Pro as well as ArcGIS Enterprise use. To configure live traffic as a utility service for your organization, see the Traffic Data section under Routing service in the Portal for ArcGIS help on the ArcGIS Enterprise website.
Historical, live, and predictive traffic data
In ArcGIS StreetMap Premium, the Speed Data Source column in the product coverage table indicates whether historical, live, or predictive traffic data exists for each country. Refer to Network Analysis coverage in the ArcGIS Online documentation for detailed descriptions of each of these traffic levels.
Historical traffic is included with the ArcGIS StreetMap Premium network dataset at no additional cost and is used as the default speed data source unless a country only has less detailed information such as speed limits or has limited street coverage available.
The historical traffic information included in the StreetMap Premium dataset is based on the average of observed speeds on a road segment over the years. This travel time data is aggregated into 5-minute intervals per day of week. So, a road may have a different travel time on Monday at 8 a.m., Monday at 8:15 a.m., or Tuesday at 8 a.m. When you perform network analysis and you set a particular day of the week or time of day, the historical traffic information is relied on to calculate the optimal route. Historical traffic data is not based solely on posted speed limits or the length of the road segment. Starting with ArcGIS StreetMap Premium 2024 releases, 5-minute intervals are available.
If a time of day is not specified for the analysis (a time-neutral case), or historical traffic information does not exist for a particular road segment, the travel time falls back to the Minutes cost attribute. The network dataset Properties > Travel Attributes > Cost > Travel Time Properties > Evaluators show the travel time evaluation fallback order, for example. The Minutes cost attribute pulls values from the Routing_Streets feature class attributes FT_Minutes and TF_Minutes (for automobiles) or FT_Truck_Minutes and TF_Truck_Minutes (for trucks).
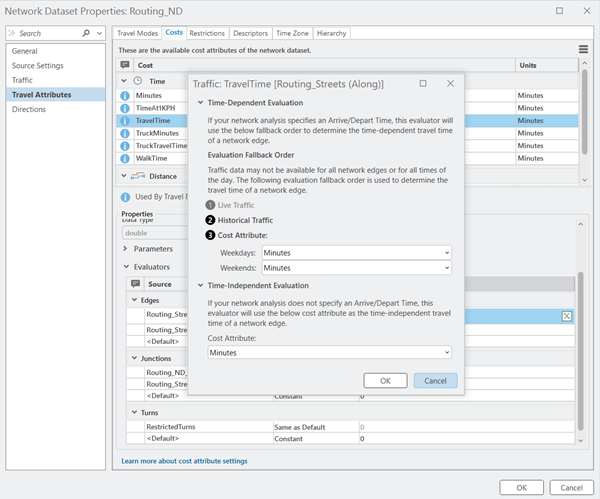
When you perform a network analysis and you set a start time that is within 1 hour of the current time, the live and predictive traffic information are used together to calculate the optimal route. Live traffic information is stored for 1 hour prior to the current time. Predictive traffic information is calculated in 15-minute intervals, extending 1 hour into the future. If there is no live traffic information for a specific roadway included in your analysis, travel speeds will default to historical traffic speeds. Also, if the start time that you specify is not within 1 hour of the current time, or the travel time in the analysis continues past the predictive data window, the analysis falls back to historical traffic speeds.
For example, if the current time is 2:30 p.m., the table below shows when historical, live, or predictive traffic will be used based on the start time of the analysis.
Analysis start time for StreetMap Premium 2024 releases
| Before 1:30 p.m. | 1:30 p.m. to 2:30 p.m. | 2:30 p.m. to 3:30 p.m. | After 3:30 p.m. |
|---|---|---|---|
Historical traffic | Live traffic and Predictive traffic (1 hour of data stored prior to the current time) | Live traffic and Predictive traffic (1 hour into the future) | Historical traffic |
Analysis start time for StreetMap Premium 2023 releases
| Before 10:30 a.m. | 10:30 a.m. to 2:30 p.m. | 2:30 p.m. to 6:30 p.m. | After 6:30 p.m. |
|---|---|---|---|
Historical traffic | Live traffic and Predictive traffic (4 hours of data stored prior to the current time) | Live traffic and Predictive traffic (4 hours into the future) | Historical traffic |
Impedance options
The available impedance options for routing are listed in the table below.
With StreetMap Premium releases, when a start time is specified, the TruckTravelTime impedance uses a combination of historical traffic information and jurisdictional truck speed limits to give more realistic travel times. If a start time is not specified, the TruckTravelTime impedance falls back to the TruckMinutes impedance logic.
Use WalkTime to model walking speed. The default speed is set to 5 kilometers per hour. To adjust the WalkTime speed on the Layer Properties dialog box, click Travel Mode > Costs > Cost Parameters. The TimeAt1KPH impedance models traveling at a constant speed of 1 kilometer per hour. The main purpose of this attribute is to support the WalkTime impedance; it is not intended to be used on its own, as walking speeds are generally not that slow.
The Minutes impedance, with or without specifying a start time, uses average speed values previously calculated from the historical traffic data. This results in quicker performance than when selecting the TravelTime impedance, which uses the actual historical traffic data based on time of day.
| Available impedance options | Description |
|---|---|
Kilometers | Find shortest route, distance wise (in kilometers). |
Miles | Find shortest route, distance wise (in miles). |
Minutes | Find shortest route, time wise, using average speed values previously calculated from the historical traffic data, which results in quicker performance. |
TimeAt1KPH | Find shortest route, time wise, using constant speed (1 kilometer per hour). |
TravelTime | Find shortest route, time wise, using automobile speed values from historical traffic data for a specific time of day. |
TruckMinutes | Find shortest route, time wise, using the smaller speed value: truck speed limit or average speed calculated from historical traffic data. |
TruckTravelTime | Find shortest route, time wise, using a combination of truck speed limits and speed values from historical traffic data for a specific time of day. |
WalkTime | Find shortest route, time wise, using adjustable walking speed. |
Restrictions
Below is a complete list of all restrictions available in the Routing_ND network dataset:
Note:
An asterisk (*) after the name indicates the restriction is turned on for Driving Time, which is the default travel mode. There are two soft restrictions available for trucks; a plus (+) after the name indicates a soft restriction.
| Name | Behavior when enabled (checked) |
|---|---|
Any Hazmat Prohibited | Avoids all roads and turns where transporting hazardous material is prohibited. |
Avoid Carpool Roads* | Avoids all roads with car pool lanes. |
Avoid Express Lanes* | Avoids all roads with express lanes. |
Avoid Ferries | Avoids all ferries. |
Avoid Gates* | Avoids all turns accessing gated roads. |
Avoid Limited Access Roads | Avoids all roads that are limited-access highways. |
Avoid Private Roads* | Avoids all roads that are not publicly owned and maintained. |
Avoid Roads Unsuitable for Pedestrians | Avoids all roads that are unsuitable for pedestrians. |
Avoid Stairways | Avoids all stairways on a pedestrian-suitable route. |
Avoid Toll Roads | Avoids all toll roads for automobiles. |
Avoid Toll Roads for Trucks | Avoids all toll roads for trucks. |
Avoid Truck Restricted Roads | Avoids all roads where trucks are prohibited unless making a local delivery. |
Avoid Unpaved Roads* | Avoids all roads that are not paved (that is, dirt, gravel, and so on). |
Axle Count Restriction | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum number of axles allowed on the road is less than the number of axles on the vehicle. |
Driving a Bus | Avoids all roads and turns where buses are prohibited. |
Driving a Taxi | Avoids all roads and turns where taxis are prohibited. |
Driving a Truck | Avoids all roads and turns where trucks are prohibited. |
Driving an Automobile* | Avoids all roads and turns where automobiles are prohibited. |
Driving an Emergency Vehicle | Avoids all roads and turns where emergency vehicles are prohibited. |
Height Restriction (meters) | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum height limit for the road is less than the vehicle height. |
Kingpin to Rear Axle Length Restriction (meters) | Avoids all roads where the maximum kingpin-to-rear-axle length limit for the road is less than the vehicle kingpin-to-rear-axle length. |
Length Restriction (meters) | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum vehicle length limit for the road is less than the vehicle length. |
Preferred for Pedestrians | Uses preferred routes suitable for pedestrian navigation. |
Riding a Motorcycle | Avoids all roads and turns where motorcycles are prohibited. |
Roads Under Construction Prohibited* | Avoids all roads that are affected by construction. |
Semi or Tractor with One or More Trailers Restriction | Avoids all roads and turns where semis or tractors with one or more trailers are restricted. |
Single-Axle Vehicles Prohibited | Avoids all roads and turns where vehicles with single axles are prohibited. |
Tandem-Axle Vehicles Prohibited | Avoids all roads and turns where vehicles with tandem axles are prohibited. |
Through Traffic Prohibited* | Avoids all roads and turns where automobile through traffic (nonlocal) is prohibited. |
Truck with Trailers Restriction | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum number of trailers allowed on a truck for the road is less than or equal to the number of trailers on the truck. |
Use Preferred Hazmat Routes+ | Uses preferred routes for transporting hazmat material (soft restriction). |
Use Preferred Truck Routes+ | Uses preferred truck routes (soft restriction). |
Walking | Avoids all roads and turns where pedestrians are prohibited. |
Weight per Axle Restriction (kilograms) | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum vehicle weight limit per axle for the road is less than the vehicle weight per axle. |
Weight Restriction (kilograms) | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum vehicle weight limit for the road is less than the vehicle weight. |
Width Restriction (meters) | Avoids all roads and turns where the maximum vehicle width limit for the road is less than the vehicle width. |
Travel modes
A travel mode is a preselected set of restrictions. The Driving Time travel mode is the default travel mode in the StreetMap Premium network dataset. The preselected set of restrictions for the Driving Time travel mode are indicated with an asterisk (*) after the restriction name in the Restrictions table above. The available travel modes for routing are listed in the following table:
| Travel mode | Description |
|---|---|
Driving Time | Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel time. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars. When you specify a start time, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where it is available. |
Driving Distance | Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel distance. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars. |
Rural Driving Time | Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel time. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars but does not discourage travel on unpaved roads. When you specify a start time, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where it is available. |
Rural Driving Distance | Models the movement of cars and other similar small automobiles, such as pickup trucks, and finds solutions that optimize travel distance. Travel obeys one-way roads, avoids illegal turns, and follows other rules that are specific to cars but does not discourage travel on unpaved roads. |
Trucking Time | Models basic truck travel by preferring designated truck routes and finds solutions that optimize travel time. Routes must obey one-way roads, avoid illegal turns, and so on. When you specify a start time, dynamic travel speeds based on traffic are used where it is available, up to the legal truck speed limit. |
Trucking Distance | Models basic truck travel by preferring designated truck routes, and finds solutions that optimize travel distance. Routes must obey one-way roads, avoid illegal turns, and so on. |
Walking Time | Follows paths and roads that allow pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel time. The walking speed is set to 5 kilometers per hour. |
Walking Distance | Follows paths and roads that allow pedestrian traffic and finds solutions that optimize travel distance. |