Summary
Appends multiple input datasets into an existing target dataset. Input datasets can be feature classes, tables, shapefiles, rasters, or annotation or dimensions feature classes.
To combine input datasets into a new output dataset, use the Merge tool.
Illustration
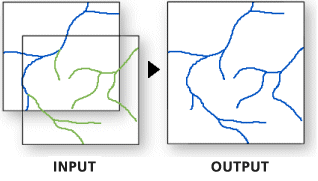
Usage
Use this tool to add new features or other data from multiple datasets to an existing dataset. This tool can append point, line, or polygon feature classes, tables, rasters, annotation feature classes, or dimensions feature classes to an existing dataset of the same type. For example, several tables can be appended to an existing table, or several rasters can be appended to an existing raster dataset, but a line feature class cannot be appended to a point feature class.
The Field Map parameter in the Append tool can be used to control how the attribute information from the input dataset fields is transferred to the target dataset. The Field Map parameter can only be used if Use the Field Map to reconcile schema differences is chosen for the Schema Type parameter.
All fields in the output dataset and the contents of those fields can be controlled using the Field map.
- To change the field order, select a field name and drag it to the preferred position.
- The default data type of an output field is the same as the data type of the first input field (of that name) it encounters. You can manually change the data type at any time to any other valid data type.
- The following merge rules are available: first, last, join, sum, mean, median, mode, minimum, maximum, standard deviation, and count.
- When using the Join merge rule, you can specify a delimiter such as a space, comma, period, dash, and so on. To use a space, make sure the pointer is at the start of the input box and press the Spacebar once.
- You can specify the start and end positions of text fields using the format option.
- Do not perform standard deviation on a single input because values cannot be divided by zero, so standard deviation is not a valid option for single inputs.
This tool will not planarize features when they are added to the target dataset. All features from both the input feature class and the target feature class will remain intact after the append, even if the features overlap. To combine, or planarize, feature geometries, use the Union tool.
If Input schema must match target schema is chosen for the Schema Type parameter (schema_type = "TEST" in Python) , the schema (field definitions) of the input datasets must match that of the target dataset for the features to be appended. If Use the Field Map to reconcile schema differences is chosen for Schema Type (schema_type = "NO_TEST" in Python), the input dataset schema (field definitions) do not need to match the target dataset. However, any fields from the input datasets that do not match the fields of the target dataset will not be mapped to the target dataset unless the mapping is explicitly set in the Field Map parameter.
Because the data of the input datasets is written to an existing target dataset that has a predefined schema (field definitions), the Field Map parameter does not allow fields to be added or removed from the target dataset.
If the spatial references of an input and target feature class do not match, the Append tool will project the features in the input feature class to the coordinate system used by the target feature class.
This tool does not perform edge matching; no adjustment to the geometry of features will be made.
Map layers can be used as Input Datasets parameter values. If a layer has a selection, only the selected records (features or table rows) are used by the Append tool.
This tool cannot use multiple input layers with the same name. To work around this limitation, use the tool dialog box browse button to browse for the full paths of each of the Input Datasets values.
To use the Subtype parameter, the target dataset must have a defined subtype field and assigned subtype codes. In the Subtype parameter, provide a subtype description to assign that subtype to all new data that is appended to the target dataset.
Syntax
arcpy.management.Append(inputs, target, {schema_type}, {field_mapping}, {subtype}, {expression})| Parameter | Explanation | Data Type |
inputs [inputs,...] | The input datasets containing the data to be appended to the target dataset. Input datasets can be point, line, or polygon feature classes, tables, rasters, annotation feature classes, or dimensions feature classes. Tables and feature classes can be combined. If a feature class is appended to a table, attributes will be transferred, but the features will be dropped. If a table is appended to a feature class, the rows from the input table will have null geometry. | Table View; Raster Layer |
target | The existing dataset where the data of the input datasets will be appended. | Table View; Raster Layer |
schema_type (Optional) | Specifies whether the fields of the input dataset must match the fields of the target dataset for data to be appended.
| String |
field_mapping (Optional) | Controls how the attribute fields from the input datasets will be transferred or mapped to the target dataset. This parameter can only be used if the schema_type parameter is NO_TEST. Because the input datasets are appended to an existing target dataset that has predefined fields, you cannot add, remove, or change the type of the fields in the field map. You can set merge rules for each output field. Merge rules allow you to specify how values from two or more input fields are merged or combined into a single output value. There are several merge rules you can use to determine how the output field will be populated with values.
In Python, you can use the FieldMappings class to define this parameter. | Field Mappings |
subtype (Optional) | The subtype description to assign to all new data that is appended to the target dataset. | String |
expression (Optional) |
The SQL expression used to select a subset of the input datasets' records. If multiple input datasets are specified, they will all be evaluated using the expression. If no records match the expression for an input dataset, no records from that dataset will be appended to the target. For more information about SQL syntax, see SQL reference for query expressions used in ArcGIS. | SQL Expression |
Derived Output
| Name | Explanation | Data Type |
| output | The updated target dataset. | Table View; Raster Layer |
Code sample
The following Python window script demonstrates how to use the Append function in immediate mode.
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data/"
arcpy.Append_management(["north.shp", "south.shp", "east.shp", "west.shp"],
"wholecity.shp", "TEST")The following script demonstrates how to use the Append function.
# Name: Append.py
# Description: Use the Append tool to combine several shapefiles
# Import system modules
import arcpy
import os
# Set environment settings
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/data"
# Set local variables
outLocation = "C:/Output"
outName = "MA_towns.shp"
schemaType = "NO_TEST"
fieldMappings = ""
subtype = ""
# Process: Create a new empty feature class to append shapefiles to
emptyFC = arcpy.CreateFeatureclass_management(outLocation, outName, "POLYGON",
"amherst.shp")
# All polygon FCs in the workspace are MA town shapefiles, you want to append
# these to the empty FC. The list will resemble ["amherst.shp", "hadley.shp",
# "pelham.shp", "coldspring.shp"]
fcList = arcpy.ListFeatureClasses("", "POLYGON")
# Create FieldMappings object to manage merge output fields
fieldMappings = arcpy.FieldMappings()
# Add the target table to the field mappings class to set the schema
fieldMappings.addTable(emptyFC)
# Add input fields for the town name to TOWNNAME field that matches the
# target dataset since each input dataset has a different field name for
# this info
fldMap = arcpy.FieldMap()
fldMap.addInputField("amherst.shp","TOWNNAME")
fldMap.addInputField("hadley.shp","NAME")
fldMap.addInputField("pelham.shp","TOWN_NAME")
fldMap.addInputField("coldspring.shp","TOWN")
# Set name of new output field "TOWNNAME"
townName = fldMap.outputField
townName.name, townName.aliasName, townName.type = "TOWNNAME", "TOWNNAME", "TEXT"
fldMap.outputField = townName
# Add output field to field mappings object
fieldMappings.addFieldMap(fldMap)
# Do the same thing for the POPULATION field
fldMap = arcpy.FieldMap()
fldMap.addInputField("amherst.shp","POPULATION")
fldMap.addInputField("hadley.shp","POP")
fldMap.addInputField("pelham.shp","POP_2010")
fldMap.addInputField("coldspring.shp","POP")
# Set name of new output field "POPULATION"
pop = fldMap.outputField
pop.name, pop.aliasName, pop.type = "POPULATION", "POPULATION", "LONG"
fldMap.outputField = pop
# Add output field to field mappings object
fieldMappings.addFieldMap(fldMap)
# Process: Append the feature classes to the empty feature class
arcpy.Append_management(fcList, os.path.join(outLocation, emptyFC), schemaType,
fieldMappings, subtype)Environments
- Preserve Global IDs
For the Append tool, this environment only applies to enterprise geodatabase data and will only work on data that has a Global ID field with a unique index. If the Global ID field does not have a unique index, the tool may fail. To add a unique index to your Global ID field, you can use the Add Attribute Index tool.
Licensing information
- Basic: Yes
- Standard: Yes
- Advanced: Yes